Should you Brush First or Floss First?

Research shows, nearly 70 percent of Americans brush their teeth twice a day, but only 40 percent floss at least once daily. However, there is a strong connection between daily flossing and good oral health.

Research shows, nearly 70 percent of Americans brush their teeth twice a day, but only 40 percent floss at least once daily. However, there is a strong connection between daily flossing and good oral health.
Braces are dental retainers used in orthodontics to align and straighten teeth. They help position the teeth about the individual’s bite. Despite the effective work these dental tools do, patients are left with one main concern. The white spot left…
The first days of having braces can be hectic. Everything would feel and seem as If you have a new permanent feature in your mouth that you just can’t get rid of. When people get braces, regardless of the benefits that they may offer, the thing they want the most would be taking them off. This is why more orthodontic patients keenly look forward to the day they will take off their braces.
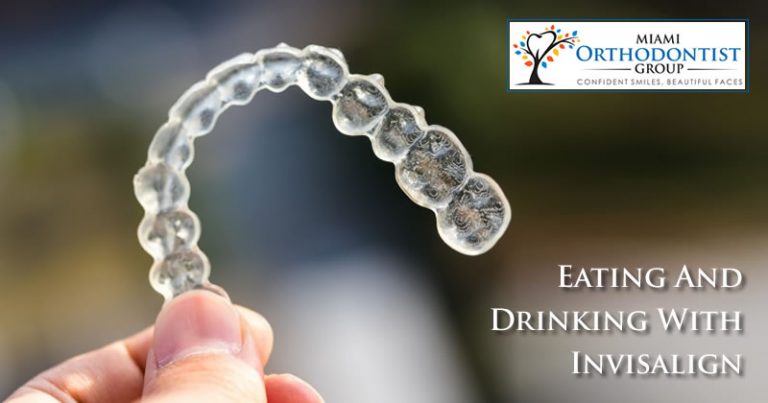

Over the years, more and more people have been using Invisalign in orthodontic treatment due to its numerous advantages. One thing about Invisalign as compared to alternatives like braces is that Invisalign is aesthetically looking perfectly blending in with your appearance. In addition to that, Invisalign is removable.

An Orthodontic treatment especially braces can be painful. The resulting pain and discomfort of having braces on can be difficult to adjust to. This is why you need quick and simple pain relief methods to help you handle and deal with the resultant pain of orthodontic treatment.

Braces and rubber bands both are very effective in straightening your teeth and for the treatment of misaligned jaw. Commonly, wearing braces is enough but in some cases, orthodontist also provides you rubber bands with braces to wear.
While wearing braces food can be easily trapped between the small spaces of braces which can cause plaque and other oral problems. So in order to avoid dental health problems follow these 4 basic tips.
Miami Orthodontist Group Blog
We firmly believe that the internet should be available and accessible to anyone, and are committed to providing a website that is accessible to the widest possible audience, regardless of circumstance and ability.
To fulfill this, we aim to adhere as strictly as possible to the World Wide Web Consortium’s (W3C) Web Content Accessibility Guidelines 2.1 (WCAG 2.1) at the AA level. These guidelines explain how to make web content accessible to people with a wide array of disabilities. Complying with those guidelines helps us ensure that the website is accessible to all people: blind people, people with motor impairments, visual impairment, cognitive disabilities, and more.
This website utilizes various technologies that are meant to make it as accessible as possible at all times. We utilize an accessibility interface that allows persons with specific disabilities to adjust the website’s UI (user interface) and design it to their personal needs.
Additionally, the website utilizes an AI-based application that runs in the background and optimizes its accessibility level constantly. This application remediates the website’s HTML, adapts Its functionality and behavior for screen-readers used by the blind users, and for keyboard functions used by individuals with motor impairments.
If you’ve found a malfunction or have ideas for improvement, we’ll be happy to hear from you. You can reach out to the website’s operators by using the following email
Our website implements the ARIA attributes (Accessible Rich Internet Applications) technique, alongside various different behavioral changes, to ensure blind users visiting with screen-readers are able to read, comprehend, and enjoy the website’s functions. As soon as a user with a screen-reader enters your site, they immediately receive a prompt to enter the Screen-Reader Profile so they can browse and operate your site effectively. Here’s how our website covers some of the most important screen-reader requirements, alongside console screenshots of code examples:
Screen-reader optimization: we run a background process that learns the website’s components from top to bottom, to ensure ongoing compliance even when updating the website. In this process, we provide screen-readers with meaningful data using the ARIA set of attributes. For example, we provide accurate form labels; descriptions for actionable icons (social media icons, search icons, cart icons, etc.); validation guidance for form inputs; element roles such as buttons, menus, modal dialogues (popups), and others. Additionally, the background process scans all the website’s images and provides an accurate and meaningful image-object-recognition-based description as an ALT (alternate text) tag for images that are not described. It will also extract texts that are embedded within the image, using an OCR (optical character recognition) technology. To turn on screen-reader adjustments at any time, users need only to press the Alt+1 keyboard combination. Screen-reader users also get automatic announcements to turn the Screen-reader mode on as soon as they enter the website.
These adjustments are compatible with all popular screen readers, including JAWS and NVDA.
Keyboard navigation optimization: The background process also adjusts the website’s HTML, and adds various behaviors using JavaScript code to make the website operable by the keyboard. This includes the ability to navigate the website using the Tab and Shift+Tab keys, operate dropdowns with the arrow keys, close them with Esc, trigger buttons and links using the Enter key, navigate between radio and checkbox elements using the arrow keys, and fill them in with the Spacebar or Enter key.Additionally, keyboard users will find quick-navigation and content-skip menus, available at any time by clicking Alt+1, or as the first elements of the site while navigating with the keyboard. The background process also handles triggered popups by moving the keyboard focus towards them as soon as they appear, and not allow the focus drift outside it.
Users can also use shortcuts such as “M” (menus), “H” (headings), “F” (forms), “B” (buttons), and “G” (graphics) to jump to specific elements.
We aim to support the widest array of browsers and assistive technologies as possible, so our users can choose the best fitting tools for them, with as few limitations as possible. Therefore, we have worked very hard to be able to support all major systems that comprise over 95% of the user market share including Google Chrome, Mozilla Firefox, Apple Safari, Opera and Microsoft Edge, JAWS and NVDA (screen readers).
Despite our very best efforts to allow anybody to adjust the website to their needs. There may still be pages or sections that are not fully accessible, are in the process of becoming accessible, or are lacking an adequate technological solution to make them accessible. Still, we are continually improving our accessibility, adding, updating and improving its options and features, and developing and adopting new technologies. All this is meant to reach the optimal level of accessibility, following technological advancements. For any assistance, please reach out to